Showing Where and How to Build Out Space Infrastructure
SVI has one specific business model: Be an integral part of upcoming space commerce opportunities.
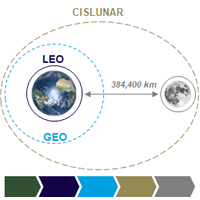
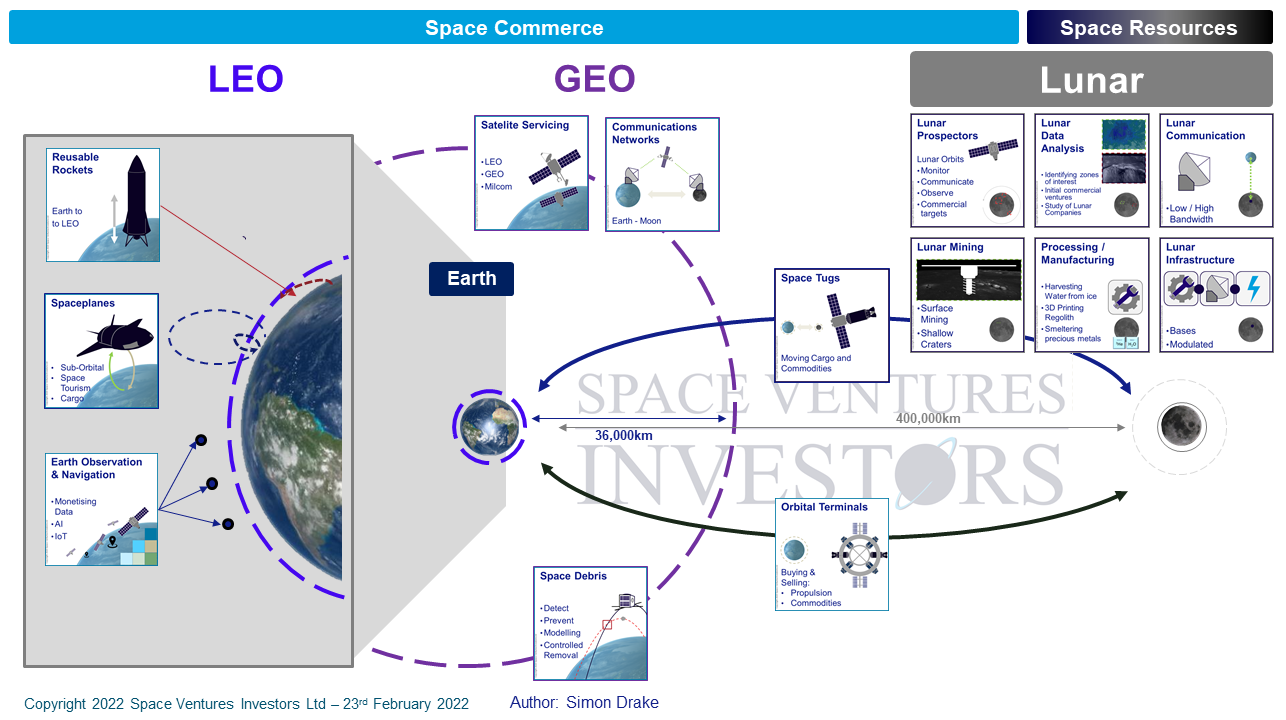
The Strategic Space Value Chain is any commercial space related business between earth and geo-synchronous orbit, focussed on low earth orbit and smaller satellites, and also includes long term commerical operations on the Moon and Near Earth Asteroids.
Well established aerospace and space companies have the expertise, sometimes government funding, and proven technology, for billion dollar space infrastructure like launch services and communications satellites.
While the goal of SVI is to be at that level in 10 years, currently the focus is on ambitious entrepreneurs and accessible technology that can open up space as a commercial market.
‣ SVI is not a Venture Capital Fund for space companies, nor is it a financial institution (like a lender).
‣ SVI may offer services, or buy into, or be a match-maker; bringing individuals, companies or syndicates to form space companies that can plan and execute highly technical operations.
‣ SVI is based in Europe, is internationally focussed, and the people and companies that invest in SVI understand the overall strategy.
Space Ventures Investors: Defining a Road Map for Strategic Space Value Chain
Next 3 Years vs Disruptive Trends
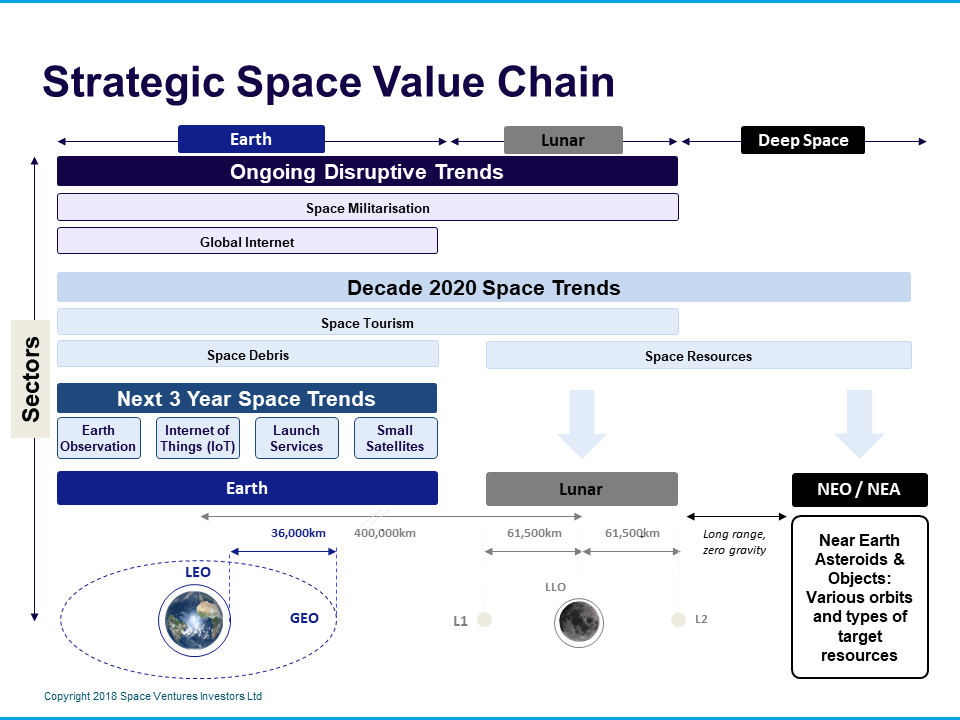
Next 3 Year Space Trends
Low Cost Launch for Europe / MENA / Asia Pacific:
‣ Sub-Orbital; CubeSat and Small Satellites
‣ Orbital (Satellites), up to 2 tonnes: Scale up to compete / disrupt established players
Making CubeSats and Small Satellites:
‣ CubeSats, ~10x10x10cm and NanoSats for research (e.g. Universities), hardware testing, space start-ups, space entrepreneurs
‣ Small Satellites (~100kg); adaptable to carrying new payloads for…
‣ Earth Observation (border and marine surveillance, environmental monitoring
‣ Internet of Things: Secure Data and Communications
‣ Increasingly sophisticated; Can maintain and potentially change orbits, therefore working for multiple clients
Data, Mass-market B2B / B2C and Niche uses
‣ From satellites for environmental monitoring, imagery, surveillance
‣ Data in space; the next step up where Big Data meets Space 2.0
Decade 2020 Space Trends
Space Resources:
‣ Lunar Operatons; Detecting substances on the Moon, extraction, and return to Earth.
‣ Asteroid Mining: Detection and classificaitn of Near Earth Asteroids and Objects, probes, extraciton of material (e.g. water) and return to an Earth orbit.
Space Debris
‣ Detection of objects
‣ Removal of debris
‣ D-orbiting devices
Space Tourism
‣ Sub-Orbital: Short horizontal lift-off trips, or ballooons.
‣ Orbital: Verticel lift off, high budget
‣ Orbiting Habitats: Commercial habitats for space tourism.